Multimedia applications extensively use 3D models. A 2D line drawing is the simplest and most straightforward way of illustrating a 3D object. It is very helpful if such a drawing can be used for generating a 3D model directly. Unfortunately, current CAD tools cannot do it, denying designers a convenient means of input. Therefore, it is highly desirable to develop algorithms that can convert a design sketch into a 3D model. Given a line drawing representing a 3D object, our approach to the conversion problem is finding face topology first and then doing 3D geometry reconstruction. Now we have developed a tool that can reconstruct complex 3D objects with planar faces and common 3D objects with curved faces from single 2D line drawings.
Highlights
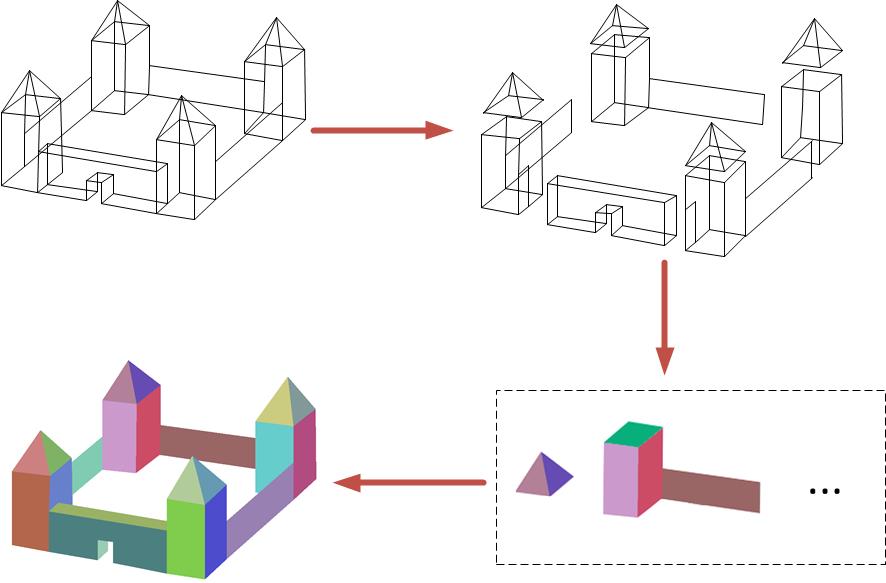
Complex 3D General Object Reconstruction from Line Drawings
L. Yang, J. Liu, X. Tang, in Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (Poster, ICCV 2013)
We propose a novel approach to 3D reconstruction of complex
general objects, including manifolds, non-manifold solids, and non-solids.
Through developing some 3D object properties, we use the degree of freedom of objects to
decompose a complex line drawing into multiple simpler
line drawings that represent meaningful building blocks of
a complex object. After 3D objects are reconstructed from
the decomposed line drawings, they are merged to form
a complex object from their touching faces, edges, and
vertices.
PDF
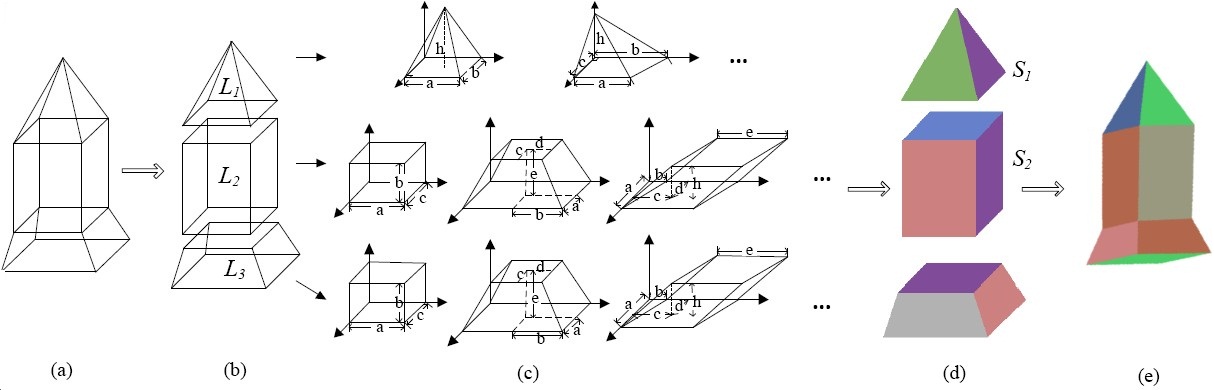
Example-Based 3D Object Reconstruction from Line Drawings
T. Xue, Y. Li, J. Liu., X. Tang, in Proceedings of IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Patter Recognition (Poster, CVPR 2012)
We propose a novel
approach, called example-based 3D object reconstruction
from line drawings, which is based on the observation that
a natural or man-made complex 3D object normally consists of a set of basic 3D objects. Given a line drawing,
a graphical model is built where each node denotes a basic object whose candidates are from a 3D model (example) database. The 3D reconstruction is solved using a maximum-a-posteriori (MAP) estimation such that the
reconstructed result best fits the line drawing.
PDF
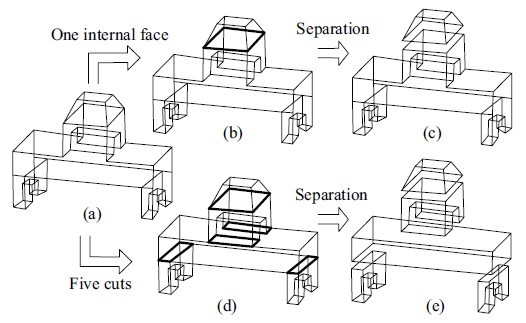
Object Cut: Complex 3D object reconstruction through line drawing separation
T. Xue, J. Liu, X. Tang, In Proceedings of IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (Poster, CVPR 2010)
Given a complex line drawing representing a solid object, our algorithm finds
the places, called cuts, to separate the line drawing into
much simpler ones. The complex 3D object is obtained by
first reconstructing the 3D objects from these simpler line
drawings and then combining them together. Several propositions
and criteria are presented for cut finding. A theorem
is given to guarantee the existence and uniqueness of the
separation of a line drawing along a cut.
PDF
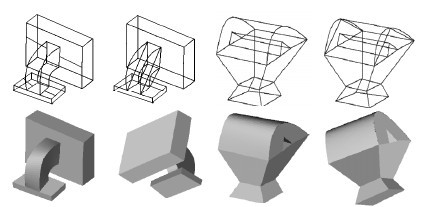
3D Reconstruction of Curved Objects from Single 2D Line Drawings
Y. Wang, Y. Chen, J. Liu, and X. Tang, In Proceedings of IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (Poster, CVPR 2008)
Previous work on 3D reconstruction from single 2D line drawings focuses on
objects with planar faces. In this paper, we propose a novel
approach to the reconstruction of solid objects that have not
only planar but also curved faces. Our approach consists of
four steps: (1) identifying the curved faces and planar faces
in a line drawing, (2) transforming the line drawing into one
with straight edges only, (3) reconstructing the 3D wireframe
of the curved object from the transformed line drawing and
the original line drawing, and (4) generating the curved faces
with Bezier patches and triangular meshes.
PDF
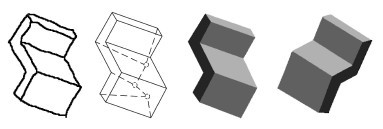
What the Back of the Object Looks Like: 3D Reconstruction from Line Drawings without Hidden Lines
L. Cao, J. Liu, and X. Tang, In IEEE Transaction on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence (PAMI), Vol. 30, pp 507-517, 2008.
This paper proposes a novel approach to reconstructing a complete 3D object,
including the shape of the back of the object, from a line drawing without hidden lines. First, we develop theoretical constraints and an
algorithm for the inference of the topology of the invisible edges and vertices of an object. Then, we present a reconstruction method
based on perceptual symmetry and planarity of the object.
PDF
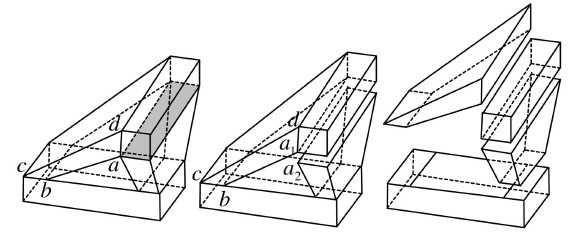
A Divide-and-Conquer Approach to 3D Object Reconstruction from Line Drawings
Y. Chen, J. Liu, and X. Tang, In Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (Poster, ICCV 2007)
In this paper, a novel approach
based on a divide-and-conquer strategy is proposed to handle
3D reconstruction of complex manifold objects from single
2D line drawings. The approach consists of three steps:
1) dividing a complex line drawing into multiple simpler
line drawings based on the result of face identification; 2)
reconstructing the 3D shapes from these simpler line drawings;
and 3) merging the 3D shapes into one complete object
represented by the original line drawing.
PDF