Image editing encompasses the processes of altering images, whether they be digital photographs, traditional analog photographs, or illustrations. Video editing is the process of editing segments of motion video production footage, special effects and sound recordings in the post production process. We mainly focused on three fundamental areas: single image haze removal, image filtering and image matting. To emphasis, we proposed the dark channel prior to effectively remove haze from a single input image, and won the 2009 CVPR Best Paper Award.
Highlights
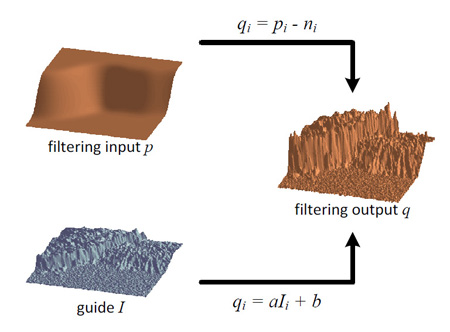
Guided Image Filtering
Kaiming He, Jian Sun, and Xiaoou Tang, IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence (TPAMI), 2012
In this paper, we propose a novel explicit image filter called guided filter. Derived from a local linear model, the guided filter
computes the filtering output by considering the content of a guidance image, which can be the input image itself or another different
image. The guided filter can be used as an edge-preserving smoothing operator like the popular bilateral filter [1], but it has better
behaviors near edges. The guided filter is also a more generic concept beyond smoothing: It can transfer the structures of the guidance
image to the filtering output, enabling new filtering applications like dehazing and guided feathering. Moreover, the guided filter
naturally has a fast and nonapproximate linear time algorithm, regardless of the kernel size and the intensity range. Currently, it is one
of the fastest edge-preserving filters. Experiments show that the guided filter is both effective and efficient in a great variety of
computer vision and computer graphics applications, including edge-aware smoothing, detail enhancement, HDR compression, image
matting/feathering, dehazing, joint psampling, etc.
PDF
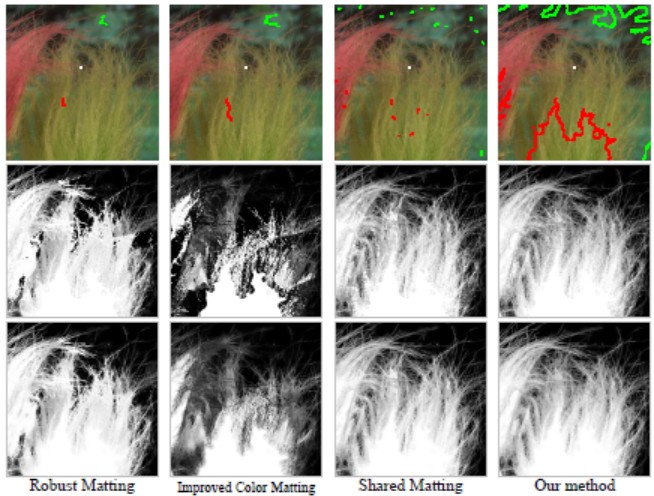
A Global Sampling Method for Alpha Matting
Kaiming He, Christoph Rhemann, Carsten Rother, Xiaoou Tang, and Jian Sun, in Proceedings of IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Patter Recognition (CVPR) 2011
Alpha matting refers to the problem of softly extracting
the foreground from an image. Given a trimap (specifying
known foreground/background and unknown pixels), a
straightforward way to compute the alpha value is to sample
some known foreground and background colors for each
unknown pixel. Existing sampling-based matting methods
often collect samples near the unknown pixels only. They
fail if good samples cannot be found nearby.
In this paper, we propose a global sampling method that
uses all samples available in the image. Our global sample
set avoids missing good samples. A simple but effective
cost function is defined to tackle the ambiguity in
the sample selection process. To handle the computational
complexity introduced by the large number of samples, we
pose the sampling task as a correspondence problem. The
correspondence search is efficiently achieved by generalizing
a randomized algorithm previously designed for patch
matching[3]. A variety of experiments show that our global
sampling method produces both visually and quantitatively
high-quality matting results.
PDF

Single Image Haze Removal using Dark Channel Prior
Kaiming He, Jian Sun, and Xiaoou Tang, IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence (TPAMI), 2010
In this paper, we propose a simple but effective image prior—dark channel prior to remove haze from a single input image.
The dark channel prior is a kind of statistics of outdoor haze-free images. It is based on a key observation—most local patches in
outdoor haze-free images contain some pixels whose intensity is very low in at least one color channel. Using this prior with the haze
imaging model, we can directly estimate the thickness of the haze and recover a high-quality haze-free image. Results on a variety of
hazy images demonstrate the power of the proposed prior. Moreover, a high-quality depth map can also be obtained as a byproduct of
haze removal.
PDF

Guided Image Filtering
Kaiming He, Jian Sun, and Xiaoou Tang, The 11th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), 2010 (Oral)
In this paper, we propose a novel type of explicit image filter guided filter. Derived from a local linear model, the guided filter
generates the filtering output by considering the content of a guidance
image, which can be the input image itself or another different image.
The guided filter can perform as an edge-preserving smoothing operator
like the popular bilateral filter [1], but has better behavior near the
edges. It also has a theoretical connection with the matting Laplacian
matrix [2], so is a more generic concept than a smoothing operator and
can better utilize the structures in the guidance image. Moreover, the
guided filter has a fast and non-approximate linear-time algorithm, whose
computational complexity is independent of the filtering kernel size. We
demonstrate that the guided filter is both effective and efficient in a great
variety of computer vision and computer graphics applications including
noise reduction, detail smoothing/enhancement, HDR compression, image
matting/feathering, haze removal, and joint upsampling.
PDF

Fast Matting using Large Kernel Matting Laplacian Matrices
Kaiming He, Jian Sun, and Xiaoou Tang, IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2010
Image matting is of great importance in both
computer vision and graphics applications. Most existing state-of-the-art techniques rely on large sparse matrices such as the matting Laplacian [12]. However, solving
these linear systems is often time-consuming, which is unfavored for the user interaction. In this paper, we propose a
fast method for high quality matting. We first derive an efficient algorithm to solve a large kernel matting Laplacian. A
large kernel propagates information more quickly and may
improve the matte quality. To further reduce running time,
we also use adaptive kernel sizes by a KD-tree trimap segmentation technique. A variety of experiments show that
our algorithm provides high quality results and is 5 to 20
times faster than previous methods.
PDF

Single Image Haze Removal using Dark Channel Prior
Kaiming He, Jian Sun, and Xiaoou Tang, IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2009 (Oral) CVPR Best Paper Award
In this paper, we propose a simple but effective
image prior - dark channel prior to remove haze from a single
input image. The dark channel prior is a kind of statistics
of the haze-free outdoor images. It is based on a key
observation - most local patches in haze-free outdoor images
contain some pixels which have very low intensities in
at least one color channel. Using this prior with the haze
imaging model, we can directly estimate the thickness of the
haze and recover a high quality haze-free image. Results on
a variety of outdoor haze images demonstrate the power of
the proposed prior. Moreover, a high quality depth map can
also be obtained as a by-product of haze removal.
PDF